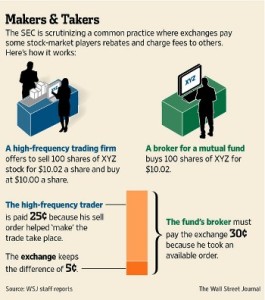
On the heels of the recent NYSE ‘outage’, which actually had little impact on overall equities trading volume, but did lead to volume spikes away from the NYSE and at competing exchanges across the fragmented marketplace, the volume also increased with regard to spirited discussions about market structure. And, whenever talking about market structure, the “rebate debate” insofar as “maker-taker” rebate and fee schemes remain a front burner topic. It is no surprise that many (but not all) sell-side brokerdealers are characteristically in favor of these complex Chinese menus offered by the assortment of major exchange venues and dark pool operators. After all, brokers are ever more dependent on these ‘rebates’ as the race to zero in terms of commission rates paid by institutional customers continues to eat into executing broker income. To counteract the business model impact on BDs, savvy executing brokers have [for a number of years] been making up for lower rates via capturing offsetting revenue from routing customer orders to those bounty-paying trade execution platforms.
On the other hand, nobody should be surprised that an increasing number of institutional investment managers from the buy-side are beginning to “get the joke”, but they aren’t laughing as many realize that brokers are effectively double-dipping by charging their customers a commission and also pocketing kickbacks from competing execution venues that pay those brokers to help light up their screens and provide so-called actionable liquidity execution.
A comprehensive database of global brokerdealers in more than 30 countries, including the US is available at www.brokerdealer.com
To wit, and in our continuing coverage of this topic, MarketsMuse curators spotlighted this week’s story from buy-side publication Pensions & Investment Magazine, which profiles the heightened concern on the part of buysiders and the growing number who are expressing their angst with the SEC, the agency that is ostensibly supposed to ensure fair market practices and protect the interests of public investors. Below are select take-aways from the P&I story.
 The Buy-Side Says: “Along with conflict-of-interest issues with rebates, other concerns like increased transaction costs and lack of transparency have added to the complexity of today’s market structure,” says Ryan Larson, RBC Global Asset Management. Added Larson, “Whether it’s SEC mandated, or better yet, driven from market participants themselves, I think it’s time to finally address the elephant in the room and start thinking about possible alternatives to the maker-taker model. … It’s not just the buy side that has been calling for a pilot on maker-taker. It’s the sell side, some of the exchanges, Congress, even members of the (SEC) as well. When you see that diverse of a group calling for change, I think it suggests something very important — whether maker-taker is the right approach. This could be one of the most impactful tests ever taken up in market structure.”
The Buy-Side Says: “Along with conflict-of-interest issues with rebates, other concerns like increased transaction costs and lack of transparency have added to the complexity of today’s market structure,” says Ryan Larson, RBC Global Asset Management. Added Larson, “Whether it’s SEC mandated, or better yet, driven from market participants themselves, I think it’s time to finally address the elephant in the room and start thinking about possible alternatives to the maker-taker model. … It’s not just the buy side that has been calling for a pilot on maker-taker. It’s the sell side, some of the exchanges, Congress, even members of the (SEC) as well. When you see that diverse of a group calling for change, I think it suggests something very important — whether maker-taker is the right approach. This could be one of the most impactful tests ever taken up in market structure.”
The Not-So-Subjective Market Data Vendor Says: “The whole point of maker-taker is to incentivize display of liquidity in lit markets,” said Henry Yegerman, director of trading analytics and research at financial data provider Markit Group Ltd., New York. “Market participants who place trades that rest passively in a venue, and so add liquidity, get a rebate. Investors who aggressively cross the spread to access that liquidity pay a fee to do so.” Institutional investors that are looking to buy or sell large blocks of stocks “are frequently takers of liquidity,” he said.
The Altruistic Sell-Side Perspective: Joseph Saluzzi, partner, co-founder and co-head of equity trading of Themis Trading LLC, a Chatham Township, N.J.-based agency broker for institutional investors said the link between liquidity and maker-taker doesn’t exist. What maker-taker does increase, Mr. Saluzzi said, is volume. “Liquidity and volume are two different things,” Mr. Saluzzi said. “Maker-taker creates volume, and a lot of that is artificial.”
Mr. Saluzzi said liquidity access is not helped through maker-taker, but by changes in a fragmented market structure that would reduce the number of trading venues. “Liquidity is not helped by rebates, but by less fragmentation,” Mr. Saluzzi said. “Maker-taker is the linchpin of the problems with the market. It’s a relic of a system that was around 15 years ago.”
The Exchange Perspective: Not Everyone Agrees: IEX, the dark-pool operator whose ATS platform is now awaiting SEC approval to operate as a regulated exchange is perhaps the most outspoken critic of maker-taker fee/rebate schemes; customers are charged a flat rate commission irrespective of how an order interacts with prevailing bid-quotes. The New York Stock Exchange came out against maker-taker rebates in testimony by exchange executives in 2014, while Nasdaq Global Markets is running a pricing test program that lowers rebate pricing for select stocks to gauge the effects on liquidity. In two reports this year on the test, Nasdaq has said the lower rebates have had a negative effect on liquidity.
At the other end of the spectrum, executives at BATS Global Markets Inc., which is perhaps the second largest equities exchange as measured by volume, don’t support an outright maker-taker ban and think the rebate paid to liquidity providers matters, “particularly with less liquid securities,” said Eric Swanson, general counsel at BATS, Kansas City, Mo.
[MarketsMuse editor note: Mr. Swanson is a former SEC senior executive who served as Asst. Director of Compliance Inspections and Examinations during the same period of time that his wife Shana Madoff-Swanson, the niece of convicted felon Bernie Madoff, received millions of dollars in compensation while she served as head of compliance for Bernard L. Madoff Investment Securities. According to Wikipedia, Swanson first met Shana Madoff when he was conducting an SEC examination of whether Bernie Madoff was running a Ponzi scheme. Ms. Madoff-Swanson’s father Peter is the brother of Bernie Madoff and is currently serving an extended sentence in a federal jail while Uncle Bernie is serving a 150-year sentence.]
The full story from P&I can be accessed by clicking this link.







